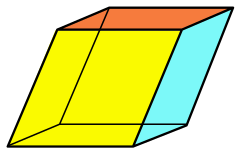
Rhombohedron
| Rhombohedron | |
|---|---|
| |
| Type | prism |
| Faces | 6 rhombi |
| Edges | 12 |
| Vertices | 8 |
| Symmetry group | Ci , [2+,2+], (×), order 2 |
| Properties | convex, equilateral, zonohedron, parallelohedron |
In geometry, a rhombohedron (also called a rhombic hexahedron[1][2] or, inaccurately, a rhomboid[a]) is a three-dimensional figure with six faces which are rhombi. It is a special case of a parallelepiped where all edges are the same length. It can be used to define the rhombohedral lattice system, a honeycomb with rhombohedral cells. A cube is a special case of a rhombohedron with all sides square.
Four points forming non-adjacent vertices of a rhombohedron necessarily form the four vertices of an orthocentric tetrahedron, and all orthocentric tetrahedra can be formed in this way.[3]
Rhombohedral lattice system[edit]
The rhombohedral lattice system has rhombohedral cells, with 6 congruent rhombic faces forming a trigonal trapezohedron:
Special cases by symmetry[edit]

| Form | Cube | Trigonal trapezohedron | Right rhombic prism | Oblique rhombic prism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle constraints |
||||
| Symmetry | Oh order 48 |
D3d order 12 |
D2h order 8 |
C2h order 4 |
| Faces | 6 squares | 6 congruent rhombi | 2 rhombi, 4 squares | 6 rhombi |
- Cube: with Oh symmetry, order 48. All faces are squares.
- Trigonal trapezohedron (rhombohedron): with D3d symmetry, order 12. All non-obtuse internal angles of the faces are equal (all faces are congruent rhombi). This can be seen by stretching a cube on its body-diagonal axis. For example, a regular octahedron with two regular tetrahedra attached on opposite faces constructs a 60 degree trigonal trapezohedron.
- Right rhombic prism: with D2h symmetry, order 8. It is constructed by two rhombi and four squares. This can be seen by stretching a cube on its face-diagonal axis. For example, two right prisms with regular triangular bases attached together makes a 60 degree right rhombic prism.
- Oblique rhombic prism: with C2h symmetry, order 4. It has only one plane of symmetry, through four vertices, and six rhombic faces.
Solid geometry[edit]
For a unit (i.e.: with side length 1) rhombohedron,[4] with rhombic acute angle , with one vertex at the origin (0, 0, 0), and with one edge lying along the x-axis, the three generating vectors are
- e1 :
- e2 :
- e3 :
The other coordinates can be obtained from vector addition[5] of the 3 direction vectors: e1 + e2 , e1 + e3 , e2 + e3 , and e1 + e2 + e3 .
The volume of a rhombohedron, in terms of its side length and its rhombic acute angle , is a simplification of the volume of a parallelepiped, and is given by
We can express the volume another way :
As the area of the (rhombic) base is given by , and as the height of a rhombohedron is given by its volume divided by the area of its base, the height of a rhombohedron in terms of its side length and its rhombic acute angle is given by
Note:
- 3 , where 3 is the third coordinate of e3 .
The body diagonal between the acute-angled vertices is the longest. By rotational symmetry about that diagonal, the other three body diagonals, between the three pairs of opposite obtuse-angled vertices, are all the same length.
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Miller, William A. (January 1989). "Maths Resource: Rhombic Dodecahedra Puzzles". Mathematics in School. 18 (1): 18–24. JSTOR 30214564.
- ^ Inchbald, Guy (July 1997). "The Archimedean honeycomb duals". The Mathematical Gazette. 81 (491): 213–219. doi:10.2307/3619198. JSTOR 3619198.
- ^ Court, N. A. (October 1934), "Notes on the orthocentric tetrahedron", American Mathematical Monthly, 41 (8): 499–502, doi:10.2307/2300415, JSTOR 2300415.
- ^ Lines, L (1965). Solid geometry: with chapters on space-lattices, sphere-packs and crystals. Dover Publications.
- ^ "Vector Addition". Wolfram. 17 May 2016. Retrieved 17 May 2016.



















